Process Safety Management
Process Safety Management (PSM) became prominent and requires methods and procedures to properly manage hazardous chemicals, with the goal of creating safe workplaces and preventing “unexpected releases of toxic, reactive, or flammable liquids and gases” that can cause disasters. Process Safety Management model is usually a blend of technology, procedures and management frameworks. The model includes up to 20 elements categorized into four pillars:
- Numbers of Corrosion Control Documents (CCD’s) completed.
- Numbers of process units with RBI completed.
- Numbers of process units with all IOW’s implemented.
- Numbers of operators trained on their CCD & IOW’s.
Control of Major Accident Hazards (COMAH) covers PSM. In the Middle East several countries have opted for Safety Management Systems (SMS), which have PSM embedded. Process safety is largely controlled through Occupational Health and Safety Acts and regulations pertaining to Dangerous Goods and Major Hazard Facilities.
Establishing Process Safety Initiatives (PSI)
- Pressure Equipment Integrity (PEI) - IOW creation process.
- Ensure Safe Production (ESP) - IOW monitoring process
- Operator Training and Procedures - IOW knowledge transfer
- Management Of Change (MOC) - IOW change process implementation
- Investigations – 3 Levels up to RCA
- Protective Instrument Systems (IPF – “SIL”)
- Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM)
- Causal Learning
- Audits and Assessments
- Process Hazards Analysis (PHA)
Corrosion Control Documents – Contents
- Relatively comprehensive documents for managing equipment degradation.
- Description of the process unit and process conditions
- Shutdown and start up conditions that may affect corrosion and degradation mechanisms, as well as normal operation
- Process Flow Diagram (PFD) and Materials and Corrosion Diagram (modified PFD showing construction materials)
- Corrosion Control Loops (areas of similar corrosion within the PFD) e.g. overhead system, slurry system, reflux system, etc.
- All potential types of degradation (and fouling) in each process unit and history of problem areas
- Quantitative and predictive models for degradation mechanisms
- Vital corrosion control procedures, injections, inhibitors, etc.
- Recommended inspection & corrosion monitoring, process changes, construction materials changes, etc
Integrity Operating Windows (IOW)
- Historical operating, maintenance & inspection records .
- Design data; lab data; operating data
- Metallurgical and corrosion data and modules
- Process chemistry and engineering knowledge
- Reactive chemistry knowledge
- Recommended practices (industry and company)
- Process and corrosion modeling tools
- Subject matter expertise and experience
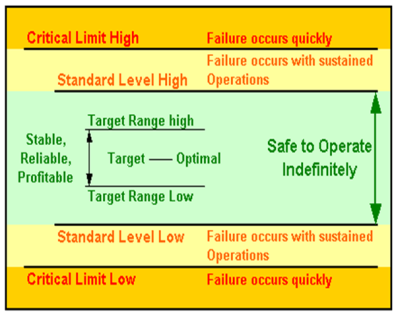
Result: Reasonable, practical IOW’s, not too conservative / not non-conservative
- A catastrophic release of hydrocarbons or hazardous fluids
- Loss of containment
- Non-orderly shutdown
- A negative impact to the long term unit performance and its ability to meet turnaround run length
- Excessive financial impact
1.Boiler Feed Water Level : Loss of boiler feed water level could quickly cause boiler tube rupture
2.Hydro-process Reactor Temperature : Metal temperatures below the MDMT could give rise to brittle fracture
3.Heater Tube Skin Temperature : Tube could rupture quickly if overheated, caused, for example, by a no flow or hot spot condition.
4.Sulfuric Acid Strength in Alkylation : Too low acid strength could cause runaway reaction.
Level 1
- Awareness and Overview of the PEI Process Safety Initiative
- SSA Video / CCD / RBI / OEMI / Operator Training
Level 2
Introduction to Corrosion Control Documents, What they contain; where they’re stored; how to use them.
Level 3
- Details contained within each operator’s unit-specific CCD
- Specific IOW’s and the reasoning behind them
- What can happen if the IOW is exceeded